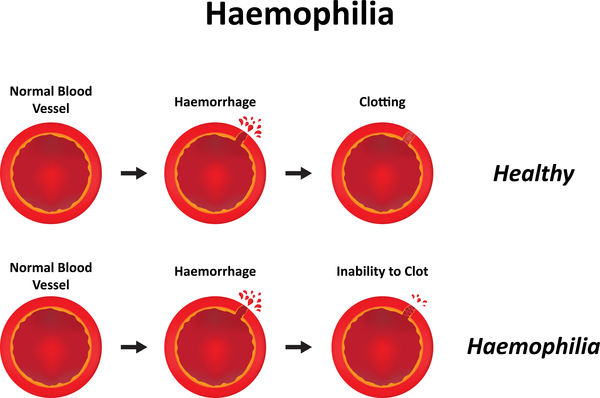
Hemophilia is a rare disorder in which your blood doesn’t clot normally because it lacks sufficient blood-clotting proteins (clotting factors). If you have hemophilia, you may bleed for a longer time after an injury than you would if your blood clotted normally. Small cuts usually aren’t much of a problem.
CAUSES OF HEMOPHILIA
Hemophilia is caused by a mutation or change, in one of the genes, that provides instructions for making the clotting factor proteins needed to form a blood clot. This change or mutation can prevent the clotting protein from working properly or to be missing altogether. These genes are located on the X chromosome.
3 MAIN TYPES OF HEMOPHILIA
The three main forms of hemophilia include the following:
- Hemophilia A: Caused by a lack of the blood clotting factor VIII; approximately 85% of hemophiliacs have type A disease.
- Hemophilia B: Caused by a deficiency of factor IX.
- Hemophilia C: Some doctors use this term to refer to a lack of clotting factor XI.
CAN HEMOPHILIA BE CURE
There is currently no cure for hemophilia. Effective treatments do exist, but they are expensive and involve lifelong injections several times per week to prevent bleeding.
FOOD TO AVOID IF YOU HAVE HEMOPHILIA
Food and supplements to avoid
- large glasses of juice.
- soft drinks, energy drinks, and sweetened tea.
- heavy gravies and sauces.
- butter, shortening, or lard.
- full-fat dairy products.
- candy.
- foods containing trans fats, including fried. foods and baked goods (pastries, pizza, pie, cookies, and crackers)
WHY HEMOPHILIA IS RARE IN FEMALE
Hemophilia is a rare blood disease that usually occurs in males. In fact, it’s extremely rare for women to be born with the condition because of the way it’s passed down genetically. A female would need to inherit two copies of the faulty gene — one from each parent — to develop hemophilia A, B or C.
SYMPTOMS OF HEMOPHILIA
The extent of your symptoms depends on the severity of your factor deficiency. People with a mild deficiency may bleed in the case of trauma. People with a severe deficiency may bleed for no reason. This is called “spontaneous bleeding.” In children with hemophilia, these symptoms may occur around age 2.
Spontaneous bleeding can cause the following:
- blood in the urine
- blood in the stool
- deep bruises
- large, unexplained bruises
- excessive bleeding
- bleeding gums
- frequent nosebleeds
- pain in the joints
- tight joints
- irritability (in children)